Dr. Ioannis Georgiou Plastic Surgeon
University of Marburg Germany
Liposuction and the technique of anaesthesia
Liposuction is the surgical technique of removing fat cells from the human body, through very small surgical incisions, a few millimetres long and with the help of very thin metal tubes and negative pressure created by the suction machine. The father of modern liposuction is the Italian doctor Giorgio Fischer, who first applied a special liposuction cannula together with a special pump in 1976. Since then, many changes have been made to the method resulting in a simpler procedure, greater safety, and more aesthetic results.
Anatomy
Fat usually makes up 15-20% of the body weight of an adult man and 20-25% of an adult woman. It occupies the space between the skin and the muscle fascia, the so-called subcutaneous tissue. Some of the functions of adipose tissue include thermal insulation, storage of fuel, high energy content and providing energy during prolonged conditions of reduced food intake.During middle age, an increase in the amount of subcutaneous fat occurs, with more pronounced deposition in the abdomen and, in general, in the area around the ‘waist’ in both men and women. In addition, in women there is an increase in the deposition in the breasts, thighs and buttocks.
Index
Liposuction is in no way a method of weight loss and a substitute for diet and exercise.The ideal candidate for liposuction must be in good physical condition and his or her weight must not exceed the ideal body weight by far.Fat deposits must be localized in specific parts of the body and be resistant to weight loss. It is generally recommended by experts that no more than 2 to 3 kg of fat should be removed at a time to avoid serious health complications for the patient.
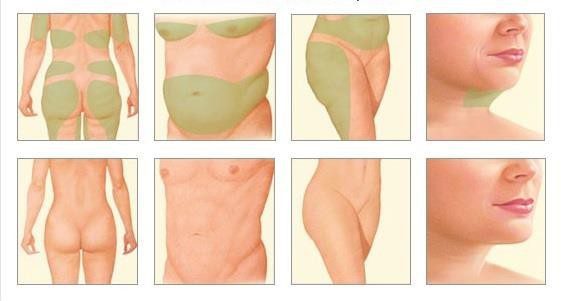
The most common areas where liposuction is done in women are the side of the thighs, i.e. the known “buns”, the buttocks, the inner knee area, the abdominal area and the face (double chin). The most common areas of liposuction in men are the chest, in cases of gynecomastia, the abdominal area, and the face (double chin) (Fig. 1). In practice, however, this operation can be performed on all parts of the body under certain conditions and always at the discretion of the attending physician.
Tumescent anaesthesia technique (Tumescent)
The technique of anaesthesia was a major milestone in liposuction and was discovered by Jeffrey Klein in 1985.It uses a solution containing saline, xylocaine (local anaesthetic), adrenaline and sodium bicarbonate.Sodium bicarbonate reduces the burning sensation caused by the bicarbonate solution’s acid pH. The addition of adrenaline to the local anaesthetic is very important because it offers important advantages: vasoconstriction, resulting in reduced absorption of the anaesthetic agent, increased duration of anaesthesia and a reduction in the total amount of dose required. In addition, vasoconstriction aids haemostasis and therefore reduces blood loss.
A large volume of fluid is slowly injected with fine needles, sometimes even three times the amount of fat to be removed. This procedure is almost painless. The patient remains in the operating room for some time until the local anaesthesia is fully effective and the area is numb.Subsequently, the plastic surgeon, through very small surgical incisions and with the help of cannulas connected to a special pump, sucks out the amount of fat tissue he considers necessary (fig. 2).
After the operation, the incisions are not sutured, but remain open to drain the fluid, resulting in less swelling, bruising and a reduced risk of inflammation.An elastic bandage is applied to facilitate drainage, which lasts 24-48 hours.A special elastic corset is then applied for a few weeks, which greatly reduces swelling. The patient is immediately mobilised and, depending on the area where the operation was performed, can return to his/her usual activities even after a few days.
Advantages
The advantages of this method over other methods such as general or regional anesthesia are the ability to anesthetize a large area safely, avoiding the risks of general anesthesia.In cases of small amounts of fat limited to a few areas of the body, liposuction is performed without the need for additional anesthesia. The subcutaneous injection of a large volume of fluid subcutaneously separates the skin from the underlying tissues and avoids damage to large vessels and nerves, minimises blood loss during the operation and prolongs analgesia for up to 24 hours postoperatively. Most importantly, the patient can return home after 30 to 60 minutes after the operation without feeling much pain and recovery is rapid.
Complementary methods
In recent years, new techniques have been used in liposuction such as lasers, ultrasound and radiofrequency in the hope of improving the ease and effectiveness of liposuction. Unfortunately, their superiority over other techniques such as the swelling technique has not yet been proven. In all three of these techniques the heat generated to liquefy fat cells can cause damage to the skin or deeper tissues or even burns. This is why their use should be limited for the time being to special cases only, always at the discretion of the surgeon in charge.
Myths and truths
It should be made clear that liposuction is not intended to reduce body weight and is not a substitute for dieting. It results in a significant reduction in volume, but not in weight. This is due to the fact that fat has a low specific gravity and its removal is not associated with a large weight reduction, which often frustrates patients who are not sufficiently informed. Also, liposuction is not indicated to fight cellulite (although surface fat absorption can help) but it does not make it worse either.Even if the patient does not change their lifestyle after surgery in terms of diet and exercise, it is very likely that they will see fat accumulate in other areas that previously did not have a problem of excessive fat cell accumulation. This is why it is imperative that after surgery the patient does not rest, but rather